Safavideriget
 Der er for få eller ingen kildehenvisninger i Ismail I § Shāh Ismā'īl I og derefter, hvilket er et problem. Du kan hjælpe ved at angive troværdige kilder til de påstande, som fremføres.
Der er for få eller ingen kildehenvisninger i Ismail I § Shāh Ismā'īl I og derefter, hvilket er et problem. Du kan hjælpe ved at angive troværdige kilder til de påstande, som fremføres.
Safavideriget | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imperium | |||||||||||||
| 1501–1736 | |||||||||||||
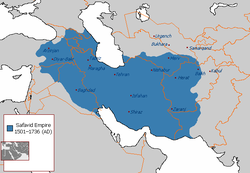 Safavideriget | |||||||||||||
| Hovedstad | Tabriz (1501-1555) Qazvin (1555-1598) Isfahan (1598-1736) | ||||||||||||
| Sprog |
| ||||||||||||
| Religion | Shia-islam | ||||||||||||
| Regeringsform | Monarki | ||||||||||||
| Shāh | |||||||||||||
• 1501-1524 | Ismā'īl I | ||||||||||||
• 1524-1576 | Tahmāsp I | ||||||||||||
• 1576-1577 | Ismā'īl II | ||||||||||||
| Muhammed Khudābanda | |||||||||||||
• 1587-1629 | 'Abbās I | ||||||||||||
• 1732-1736 | 'Abbās III (sidste) | ||||||||||||
| Shāh (de facto) | |||||||||||||
| Mahmud Hotaki | |||||||||||||
• 1725-1729 | Ashraf Khan Hotaki | ||||||||||||
| Historie | |||||||||||||
• Grundlæggelse | 1501 | ||||||||||||
• Opløsning | 1736 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
Safavideriget (persisk: دولت صفوی eller دولت صفویه, tyrkisk: Safevî Devleti, aserbajdsjansk: Səfəvilər Dövləti, صفویلر, kurdisk: Dewleta Sefewî, georgisk: სეფიანთა დინასტია) var et shia-muslimsk dynasti af kurdisk oprindelse [11] der var et af de mest betydningsfulde dynastier i Iran. Det er også begyndelsen af moderne iransk historie.[12] Safavideriget blev et af de største iranske imperier siden den muslimske erobring af Persien[13][14][15][16]. Safaviderne regerede fra 1501 til 1722 og igen fra 1729 til 1736. Under dets største udbredelse kontrollerede det hele det moderne Iran, Aserbajdsjan og Armenien, det meste af Irak, Georgien, Afghanistan, og Kaukasus, dele af Pakistan, Tadjikistan, Turkmenistan, Tyrkiet, og Usbekistan.
Safaviderne var den direkte årsag til, at shia-islam i så høj grad er udbredt i store dele af Vestasien og Kaukasus. Det var én af grundene til at Safavideriget blev anset som en trussel af det sunnitiske Osmannerrige. Det har flere gange resulteret i krig mellem de to stater.
Baggrund
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]Safaviderigets grundlæggelse var et resultat af safaviyya-ordenens militarisering siden 1400-tallet. Safaviderne har navn fra grundlæggeren af safaviyya-ordenen, Sheik Safī al-Dīn (1252 – 1334). Slægten stammer fra Fīrūz Shāh Zarrīn Kulāh, som var en seyyid (efterkommer af Profeten Muhammed), der flygtede fra Yemen og bosatte sig i Rangin i Iran i 1174.[17]
Andre kilder hævder dog, at safaviderne havde kurdiske rødder[18] eller rødder af lokalt iransk herkomst[19][20], som dog gradvist blev tyrkificeret op til grundlæggelsen af Safavideriget og derfor endte med at have tyrkisk eller aserbajdsjansk som modersmål.[21][22]
Fra deres base i Ardabil etablerede safaviderne kontrol over hele Storiran og sikrede på ny en samlet iransk identitet i regionen.[23] Riget blev dermed det første indfødte dynasti siden Sassanideriget til at etablere en forenet iransk stat.[24]
Shāh Ismā'īl I
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]Med støtte fra sine trofaste tilhængere, qizilbāsh'erne, grundlagde Shāh Ismā'īl som 14-årig Safavideriget i 1501. I de næste ti år udvidede han sit rige fra Østanatolien i vest til Khurāsān i øst. Shāh Ismā'īl tabte ikke nogen krig med undtagelse af nederlaget til Osmannerriget i 1514. Det resulterede i at han afstod Østanatolien til osmannerne. Det lykkedes Shāh Ismā'īl at fastholde resten af rigets grænser til sin død i 1524.
Shāh Tahmāsp I
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]Shāh Tahmāsp, som hidtil havde været guvernør af Herat, arvede tronen ved sin far Ismā'īls død i 1524. Han regerede til 1576 og blev den længst herskende safavidiske shāh. Tiden under Shāh Tahmāsp var præget af angreb fra både vest og øst. Osmannerne angreb Safavideriget fire gange under Suleimān I og usbekerne angreb de østlige provinser fem gange. Det betød at Safavideriget mistede territorium i Irak og at Tahmāsp blev nødt til at flytte hovedstaden fra Tabriz til Qazvin. I 1555 indgik Tahmāsp Amasya-traktaten med Osmannerriget; det satte en stopper for krige i hans levetid. Efter Tahmāsps død var der strid mellem qizilbāsh-soldaterne om, hvem der skulle lede riget. Det førte til at Ismā'īl II kom på tronen (1576-1577) og efter ham Muhammad Khudābanda (1578-87).
Shah ‘Abbās I
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]Safavideriget fandt igen styrke under Shah ‘Abbās I. Han erkendte, at den safavidiske hær, som havde lidt nederlag de seneste år, var blevet ineffektiv. Derfor reorganiserede han den, så den levede op til tidens standard. Det betød, at han måtte distancere sig fra qizilbāsh-soldaterne, som efterhånden havde tilegnet sig magt. Qizilbāsh'erne i administrationen og militæret blev gradvist skiftet ud med de nye og mere loyale ghulām'er (slaver), som var tjerkessiske, georgiske og armenske soldater, som var konverteret til islam. Fra 1598 til 1623 lykkedes det Shāh 'Abbās at generobre områder, som riget havde tabt, og fordrive portugiserne fra Den Persiske Golf.
Nedgang
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]Herskerne efter 'Abbās I var bortset fra Abbas II unyttige ledere, hvoraf nogle ikke viste særlig interesse for at styre landet. Det betød at Safavideriget efter 'Abbās II's død i 1666 blev præget af svaghed. Det kulminerede i 1722, hvor afghaneren Mir Māhmud Hotaki (1697-1725) væltede shahen, Sultān Husayn (1668-1726). Fra 1722 til 1729 blev Safavideriget de facto ledet af afghanske hotakier. I 1729 lykkedes det den safavidiske Tahmāsp II at få magt over det meste af landet, men han blev i 1732 afsat af kommandør Nāder Khān, som gjorde Tahmāsp II's søn 'Abbās III til konge. Selv om 'Abbās II officielt var konge, var det egentlig Nāder Khān som regerede landet til 1736, hvor han kronede sig selv som konge og gjorde en ende på det safavidiske dynasti.
Referencer
[redigér | rediger kildetekst]- ^ Roemer, H. R. (1986). "The Safavid Period". The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol. 6: The Timurid and Safavid Periods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 189–350. ISBN 0-521-20094-6, p. 331: "Depressing though the condition in the country may have been at the time of the fall of Safavids, they cannot be allowed to overshadow the achievements of the dynasty, which was in many respects to prove essential factors in the development of Persia in modern times. These include the maintenance of Persian as the official language and of the present-day boundaries of the country, adherence to the Twelever Shi'i, the monarchical system, the planning and architectural features of the urban centers, the centralised administration of the state, the alliance of the Shi'i Ulama with the merchant bazaars, and the symbiosis of the Persian-speaking population with important non-Persian, especially Turkish speaking minorities".
- ^ a b c Rudi Matthee, "Safavids" in Encyclopædia Iranica, accessed on April 4, 2010. "The Persian focus is also reflected in the fact that theological works also began to be composed in the Persian language and in that Persian verses replaced Arabic on the coins." "The political system that emerged under them had overlapping political and religious boundaries and a core language, Persian, which served as the literary tongue, and even began to replace Arabic as the vehicle for theological discourse".
- ^ Ronald W Ferrier, The Arts of Persia. Yale University Press. 1989, p. 9.
- ^ a b John R Perry, "Turkic-Iranian contacts", Encyclopædia Iranica, January 24, 2006: "...written Persian, the language of high literature and civil administration, remained virtually unaffected in status and content"
- ^ Cyril Glassé (ed.), The New Encyclopedia of Islam, Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, revised ed., 2003, ISBN 0-7591-0190-6, p. 392: "Shah Abbas moved his capital from Qazvin to Isfahan. His reigned marked the peak of Safavid dynasty's achievement in art, diplomacy, and commerce. It was probably around this time that the court, which originally spoke a Turkic language, began to use Persian"
- ^ Arnold J. Toynbee, A Study of History, V, pp. 514-15. excerpt: "in the heyday of the Mughal, Safawi, and Ottoman regimes New Persian was being patronized as the language of literae humaniores by the ruling element over the whole of this huge realm, while it was also being employed as the official language of administration in those two-thirds of its realm that lay within the Safawi and the Mughal frontiers"
- ^ a b Mazzaoui, Michel B; Canfield, Robert (2002). "Islamic Culture and Literature in Iran and Central Asia in the early modern period". Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective. Cambridge University Press. s. 86-7. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5.
Safavid power with its distinctive Persian-Shi'i culture, however, remained a middle ground between its two mighty Turkish neighbors. The Safavid state, which lasted at least until 1722, was essentially a "Turkish" dynasty, with Azeri Turkish (Azerbaijan being the family's home base) as the language of the rulers and the court as well as the Qizilbash military establishment. Shah Ismail wrote poetry in Turkish. The administration nevertheless was Persian, and the Persian language was the vehicle of diplomatic correspondence (insha'), of belles-lettres (adab), and of history (tarikh).
- ^ Ruda Jurdi Abisaab. "Iran and Pre-Independence Lebanon" in Houchang Esfandiar Chehabi, Distant Relations: Iran and Lebanon in the Last 500 Years, IB Tauris 2006, p. 76: "Although the Arabic language was still the medium for religious scholastic expression, it was precisely under the Safavids that hadith complications and doctrinal works of all sorts were being translated to Persian. The 'Amili (Lebanese scholars of Shi'i faith) operating through the Court-based religious posts, were forced to master the Persian language; their students translated their instructions into Persian. Persianization went hand in hand with the popularization of 'mainstream' Shi'i belief."
- ^ Savory, Roger (2007). Iran Under the Safavids. Cambridge University Press. s. 213. ISBN 978-0-521-04251-2.
qizilbash normally spoke Azari brand of Turkish at court, as did the Safavid shahs themselves; lack of familiarity with the Persian language may have contributed to the decline from the pure classical standards of former times
- ^ Zabiollah Safa (1986), "Persian Literature in the Safavid Period", The Cambridge History of Iran, vol. 6: The Timurid and Safavid Periods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-20094-6, pp. 948–65. P. 950: "In day-to-day affairs, the language chiefly used at the Safavid court and by the great military and political officers, as well as the religious dignitaries, was Turkish, not Persian; and the last class of persons wrote their religious works mainly in Arabic. Those who wrote in Persian were either lacking in proper tuition in this tongue, or wrote outside Iran and hence at a distance from centers where Persian was the accepted vernacular, endued with that vitality and susceptibility to skill in its use which a language can have only in places where it truly belongs."
- ^ Empires: Safavid and Qajar | Encyclopedia.com
- ^ "SAFAVID DYNASTY". Encyclopædia Iranica.
- ^ Helen Chapin Metz. Iran, a Country study. 1989. University of Michigan, p. 313.
- ^ Emory C. Bogle. Islam: Origin and Belief. University of Texas Press. 1989, p. 145.
- ^ Stanford Jay Shaw. History of the Ottoman Empire. Cambridge University Press. 1977, p. 77.
- ^ Andrew J. Newman, Safavid Iran: Rebirth of a Persian Empire, IB Tauris (March 30, 2006).
- ^ Walter Hinz: Uzun Hasan ve Şeyh Cüneyd – XV. Yüzyılda İran'ın Millî bir Devlet Haline Yükselişi, Türk Tarih Kurumu, 1992, s. 109
- ^ RM Savory. Ebn Bazzaz. Encyclopædia Iranica
- ^ Minorsky, V (2009). "Adgharbaydjan (Azarbaydjan)". I Berman, P; Bianquis, Th; Bosworth, CE; van Donzel, E; Henrichs, WP (red.). Encyclopedia of Islam (2nd udgave). NL: Brill. Arkiveret fra originalen 28. juli 2012. Hentet 18. maj 2013.
After 907/1502, Adharbayjan became the chielf bulwark and rallying ground of the Safawids, themselves natives of Ardabil and originally speaking the local Iranian dialect
- ^ Roger M. Savory. "Safavids" in Peter Burke, Irfan Habib, Halil İnalcık: History of Humanity-Scientific and Cultural Development: From the Sixteenth to the Eighteenth Century, Taylor & Francis. 1999, p. 259: "From the evidence available at the present time, it is certain that the Safavid family was of indigenous Iranian stock, and not of Turkish ancestry as it is sometimes claimed. It is probable that the family originated in Persian Kurdistan, and later moved to Azerbaijan, where they adopted the Azari form of Turkish spoken there, and eventually settled in the small town of Ardabil sometimes during the eleventh century."
- ^ "Peoples of Iran" Encyclopædia Iranica. RN Frye.
- ^ Peter B. Golden: An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples; In: Osman Karatay, Ankara 2002, p.321
- ^ Why is there such confusion about the origins of this important dynasty, which reasserted Iranian identity and established an independent Iranian state after eight and a half centuries of rule by foreign dynasties? RM Savory, Iran under the Safavids (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1980), p. 3.
- ^ Alireza Shapur Shahbazi (2005), "The History of the Idea of Iran", in Vesta Curtis ed., Birth of the Persian Empire, IB Tauris, London, p. 108: "Similarly the collapse of Sassanian Eranshahr in AD 650 did not end Iranians' national idea. The name "Iran" disappeared from official records of the Saffarids, Samanids, Buyids, Saljuqs and their successor. But one unofficially used the name Iran, Eranshahr, and similar national designations, particularly Mamalek-e Iran or "Iranian lands", which exactly translated the old Avestan term Ariyanam Daihunam. On the other hand, when the Safavids (not Reza Shah, as is popularly assumed) revived a national state officially known as Iran, bureaucratic usage in the Ottoman empire and even Iran itself could still refer to it by other descriptive and traditional appellations".
 |
Wikimedia Commons har medier relateret til: |


